The “Great Turkish Purge” launched by President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s Islamist, autocratic government in the aftermath of a coup attempt in July surprised many in its size. It should not have done. The failed putsch gave Erdogan’s government a golden opportunity to advance his crackdown on dissent of every kind. No wonder Erdogan, on the night of the attempt, said: “This [coup attempt] is a gift of God”.
In its annual “Freedom in the World” report, entitled “Populists and Autocrats: The Dual Threat to Global Democracy,” the Washington-based Freedom House said on January 31 that Turkey suffered the largest decline in freedoms among 195 countries over the past year. Turkey’s aggregate score declined 15 points to 38 out of 100 (the most free) — from having been in 53rd place in the 2016 report. It did manage to maintain its “partly free” status for “freedoms” together with 59 other countries. “[A]n attempted coup in July… led the government to declare a state of emergency and carry out mass arrests and firings of civil servants, academics, journalists, opposition figures, and other perceived enemies,” the report said.
Education Minister Ismet Yilmaz said that a total of 33,065 personnel have been dismissed from his ministry, most of them teachers, educators and administrative staff. Of those purged, 3,855 have been detained on charges of “terrorism”.
Qualitatively speaking, the situation at Turkish universities is no better. Most university presidents, appointed by Erdogan, staunchly ally with his party politics and dismiss academics they view as “Erdogan’s political adversaries.”
In the aftermath of a military coup d’état on September 12, 1980 (the third time the military took over in modern Turkish history), the generals issued decree no. 1402, dismissing a total of 120 scholars from the universities. By comparison, on February 7, Turkey’s “civilian” government issued a decree purging 330 scholars from universities. Erdogan’s public sector purge now amounts to around 100,000 officials, including nearly 5,000 university scholars. In other words, Erdogan’s academic purge is 38 times bigger in size than the generals’ after the 1980 coup. According to data compiled by Turkey Purge, PEN International, the Committee to Protect Journalists and the Stockholm Center for Freedom, 128,398 people have been sacked, while 91,658 are being detained.
Worse, neither the academics on the purge list nor their students were allowed to protest peacefully. Their attempted protest on February 10 at the School of Political Sciences in Ankara met a huge police force and was crushed. In the brawl, the police attacked the crowd; many in it were injured, manhandled, trapped in their robes and dragged along the ground.
One of the purged, Professor Yuksel Taskin, from an Istanbul department of journalism, tweeted: “This is a pure political ‘cleansing’. But my conscience is clear. Let my students know that I shall never, ever bow down!”
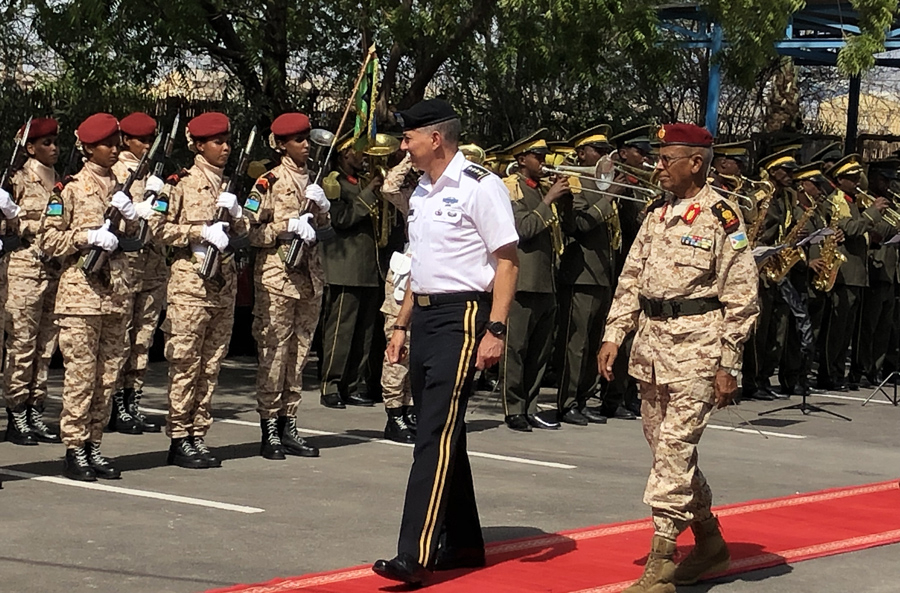

Professor Yuksel Taskin, who was recently purged from an Istanbul department of journalism, tweeted: “This is a pure political ‘cleansing’. But my conscience is clear. Let my students know that I shall never, ever bow down!” (Image source: Hakan YÜCEL video screenshot) |
Emre Tansu Keten, from the same school, wrote: “I am simply proud to be in the same list along with my senior colleagues who are thrown out because of the opinion they expressed.”
Turkish journalist Yavuz Baydar commented:
“Widening more by each and every decree, this is now a country resembling Germany of 1930, which ended up chasing out its elite beyond its borders. What I know for certain, that there will no longer be any possibilities for our academicians ‘cleansed’ to find work and, live in decency and honor.”
Baydar is not the only person to feel that the situation in Turkey increasingly resembles Nazi Germany. Melih Kirlidog, a Turkish scholar specializing in internet censorship and surveillance, said: “It resembles the atmosphere of 1933 Germany to me.”
Similarly, prominent Turkish novelist Zulfu Livaneli, who was imprisoned several times during the 1971 coup in Turkey, thinks the comparison is justified: “Some [scholars] resist, some collaborate with the regime so as to continue their work, and some turn a blind eye in silence.”
After he came to power in November 2002, Erdogan promised to make Turkey a land of freedoms, devoid of the military’s tutelage. Since then, he has tamed the once-secular military establishment. Nevertheless, his Islamist “land of freedoms” vision has only been partially materialized: You have all the freedoms you want — so long as you are a pro-Erdogan Islamist.
Burak Bekdil, one of Turkey’s leading journalists, was just fired from Turkey’s leading newspaper after 29 years, for writing what was taking place in Turkey for Gatestone. He is a Fellow at the Middle East Forum.