It is considered a fundamental principle in liberal democracies that individuals should have equality under the law, with equal access to justice, despite race, gender, or religious belief and that the same laws of a single legal system should apply equally to everyone.
To have two simultaneously functioning rules of law, applied on differing judicial bases, would create a challenge of which precedents to follow, or why individuals from different groups should be treated differently. How long before people form one group would claim to be from a different group to be exempt from the first group’s laws? Such a system invites abuse.
Dealing with minorities by differing legal systems rather than creating a more pluralist utopia simply leads to a divided society in which minorities and majorities have justified mutual distrust.
Sadly, these principles which have sculpted a strong judicial system in the United Kingdom for so long are now facing a significant threat.
In Britain, the Human Rights Act 1998 (HRA) recognises and protects women’s rights to equality, and not to be discriminated against in legal proceedings. But the rule of law in Britain is being eroded by the legitimisation of sharia councils. This has occurred under the Arbitration Act (1996), even though their operation in the Britain has been recorded since 1992.
There are valid reasons why sharia councils and sharia itself should not be given any legitimacy under British law.
First, these alternative judicial systems can mislead Muslim women to believe that sharia, and the fatwas pronounced by clerics, are binding and that such a marriage is recognised under UK law. In fact, it is estimated that 70-75% of all Islamic marriages in Britain are not recognized, according to the findings in the Dame Louise Casey report.
Islamic women also might be misled into believing that they have more marital rights than they actually have – a cruel deception that must end. And they further seem misled into believing they are compelled to approach a sharia council, rather than a UK civil court, for a divorce.
Second, these sharia councils often offer themselves as “an alternative,” to people seeking a civil law judgement, but the elders who hold the proceedings do not use juridical standards compatible with existing British legal ones. In cases arbitrated by sharia councils, as opposed to British law, for example, women lack the legal ability to initiate any divorce proceedings without the explicit agreement of her husband, and often women have no legal representation at these trials.
With little ability even to mount a legal defence, there is always the probability that Muslim women are not receiving equal justice under the law.
A report by Machteld Zee, a Dutch Academic raised the issue that sharia councils “frustrate women in their requests [for divorce], especially if the husband is unwilling to co-operate” and she also suggested that women are treated as “second-class citizens.”
sharia councils can also fundamentally attack the rights of women in arbitration, a device meant to be facilitate resolving issues. sharia councils, however, can demand that the parties involved in a dispute sign contracts beforehand, demanding that women agree to the results of the arbitration. To force a woman, who has been denied rights to any legal representation, to agree to an illegal or wrongful contract before trial, is a travesty that the British justice system cannot allow to continue.
Is it really acceptable that these sharia councils are granted authority under the Arbitration Act of 1996 when they treat women in such a way?
Dr Taj Hargey, Imam of the Oxford Islamic Congregation argues, “Sharia is not divine law, it is just medieval opinion.”
The right of a woman to be free from abuse should be a paramount consideration. Therefore, a parallel legal system that declines to recognise the law of the land on the abuse of women is fundamentally incompatible with our legal system.
Third, which law? A trial can be considered just in terms of sharia law might well not be considered just under another form of law. Even if women are allowed to attend sharia councils in Britain, their submissions in sharia law are considered worth half of the submissions of a man — not exactly fair.
Fourth, a recent report compiled by Dame Louise Casey suggests that the growth of sharia councils in Britain have increased division and segregation in communities.
What if a woman wishes to appeal the verdict? There is no right to appeal. What if she feels there was irregularity or corruption in the process? As there exists no regulator, Muslim women seem trapped in a system the outcome of which they have to accept, even when there may not even be fleeting chance of justice.
Read this ruling from a British sharia council:
1) Adultery is one of the most heinous crimes in Islamic law, the punishment for which is death by stoning. But as Britain is not a Muslim state such a punishment may not be carried out here. This punishment can only be administered in a Muslim state after due process.
This is cause for concern. This ruling actually reveals to the husband the process required to have his wife stoned to death. It arguably even encouraging men to have their wives taken abroad and have them murdered.
Is Britain really agreeing to allow women to be sentenced in England then to be stoned to death elsewhere? The ruling should instead be considered incitement to violence and reckless endangerment.
The judgement continues to state that, “Allah will punish her for her immorality.” This presumes that the wife is guilty without even hearing her testimony. The court has therefore condemned someone to murder solely the words of her husband without allowing her a chance to speak. This sort of trial has no place in a modern democracy.
It is also hard to hold sharia councils accountable: they do not record their judgements, or transparently display a record of council rulings. Why would an organisation wish not to make its rulings publicly available unless it I trying to hide something?
If cases are arbitrated on any basis that that withhold full transparency or that promotes inequality for women, it is the duty of the state not only to criticise these trials, but to withdraw any legislation that gives these laws legitimacy.
Sharia councils have been known completely to disregard the decrees of civil British courts; some councils are even suggesting that women comply with abusive husbands. More dangerously, sharia councils have even made private statements, supposedly hidden by court decree, concerning individuals in abusive relationships, public. Sharia councils have put these statements on court documents and sent them to the abuser – a practice that has led to death threats, children kidnapped, and even to women being violently raped in retaliation for seeking justice.
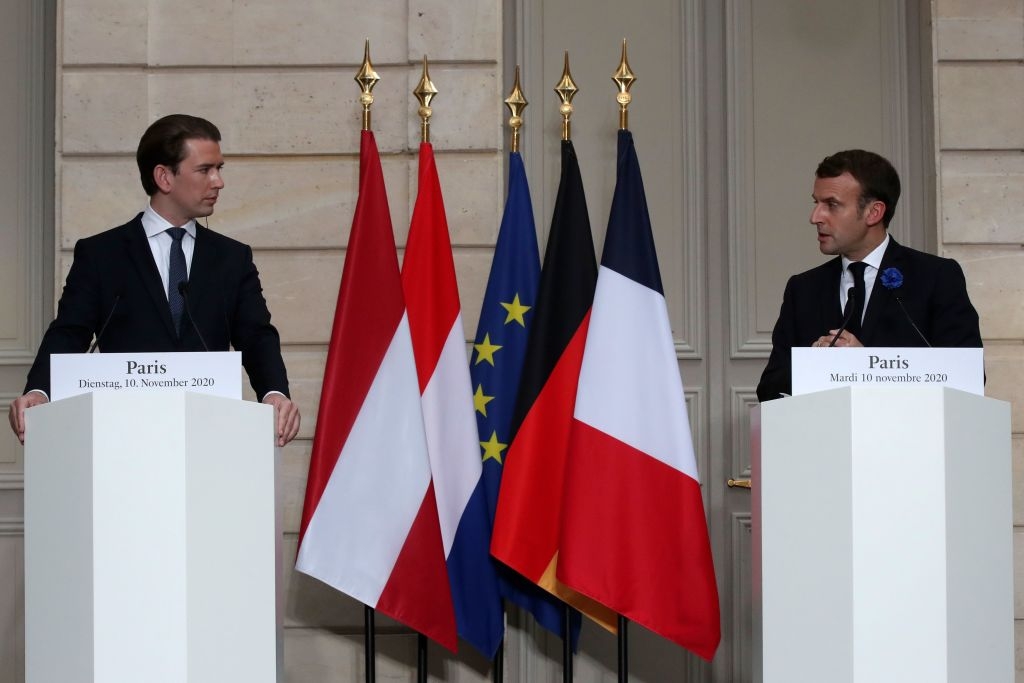

Haitham al-Haddad is a British shari’a council judge, and sits on the board of advisors for the Islamic Sharia Council. Regarding the handling of domestic violence cases, he stated in an interview, “A man should not be questioned why he hit his wife, because this is something between them. Leave them alone. They can sort their matters among themselves.” (Image source: Channel 4 News video screenshot) |
To add insult to injury, these unaccountable courts that offer judgements which sometimes incite violence and often disadvantage women, are often registered charities that charge around £800 for a divorce. How can these groups that not only fail to protect the rights of women but actually undermine them be considered charitable organisations, funded by British taxpayers?
Even more problematic is this excessive fee, when Islamic women often coming from economically disadvantaged backgrounds, and who perhaps have been discouraged from earning a living outside the home and may therefore have no funds to buy her freedom? Muslim women within abusive marriages can therefore be imprisoned by a process that is unattainable. One might even deduce that perhaps that is the purpose of the fee?
Elham Manea, author of the book Women and Sharia Law, argues that the first Sharia councils were established by Islamists. She also notes that Sharia councils have “been working with a kind of a tacit approval of British establishment. There is a certain kind of hesitancy from British institutions to interfere in what they consider is internal affair to the Muslim community.”
We can no longer be afraid to speak out against a legal system that disadvantages women because of the religion of those who run it, or that criticism may be perceived as hateful.
More alarming is that views on Sharia amongst the UK Islamic community are favourable towards this judicial practice. Sharia is now even being promoted as a solution that should be considered by the British Government. In polls conducted for the Police Exchange: 43% said they supported “the introduction of Sharia Law.” And 16% of British Muslims “strongly support” the “introduction of aspects of Sharia law into Britain”
What aspects of the Sharia do they support? How you can support only “aspects” of Sharia, when Sharia is designed to be followed in its entirety, without concession. Even then, which aspects do they support? Those that instruct that “women are restricted in leaving their homes and driving cars”? Or that “a man may coerce his wife to have sex”? Or the “recommendation of severe punishments for homosexuals?”
48% of the respondents said they would not turn someone they know with links to terrorism in Syria over to the police.
As Denis MacEoin illustrates, Sharia even justifies jihad:
In Sharia Law or One Law for All, I drew attention to another level of sharia rulings that provide fatwas for numbers of British Muslims, in particular of the younger generation. These are online sites: “fatwa banks.” Individuals or couples send questions to the muftis who run the sites, and receive answers in the form of fatwas that are considered authoritative. The questions and answers are preserved in galleries of rulings, which can be browsed by anyone seeking advice. The sites are by no means consistent, differing from one scholar to another. But they do provide an insight into the kinds of rulings that may be given in the sharia councils.
Among the rulings MacEoin details is that “fighting the Americans and British is a religious duty.” Such a ruling, sadly, could be delivered on British soil.
Sharia councils and Sharia both clearly restrict the rights of women, homosexuals, Christians and Jews, and are therefore incompatible with a diverse and tolerant society. They should be granted no legitimacy by the state.
The cessation of Sharia councils in the UK is not Islamophobic, or an “attack on Islamic rights to freedom of expression or belief”. It is the defence of a just legal system that respects diversity but judges all equally. If we are to have a society in which all are equal, then all law must be derived from a single system that applies to all.
Robbie Travers, a political commentator and consultant, is Executive Director of Agora, former media manager at the Human Security Centre, and a law student at the University of Edinburgh.