Journalism in Turkey: Newsroom vs. Courtroom by Burak Bekdil

- According to a report by the Turkish Journalists Association, 500 journalists were fired in Turkey in 2015; 70 others were subjected to physical violence. Thirty journalists remain in prison, mostly on charges of “terrorism.” There are also many journalists among the 1,845 Turks who have been investigated or prosecuted for insulting President Recep Tayyip Erdogan since he was elected in August 2014.
-
- After the secular daily newspaper Cumhuriyet published evidence of arms deliveries by the Turkish intelligence services to Islamist groups in Syria, President Erdogan himself filed a criminal complaint against Cumhuriyet’s editor-in-chief, Can Dundar, and the Ankara bureau chief, Erdem Gul.
- At a March 25 hearing, the Istanbul court ruled for the whole trial to be held in secret.
- “We came here today to defend journalism…We said we would defend the people’s right to access information. We defended that and we were arrested.” — Can Dundar, editor-in-chief of Cumhuriyet.
- The trial clearly exhibits how Erdogan’s authoritarian rule diverges from Western democratic culture.
“Turkey is where many journalists may have to spend more time at their attorneys’ offices or in courtrooms than in the newsrooms, where they should be,” a Western diplomat joked bitterly. “Don’t quote me on that. I don’t want to be declared persona non grata,” he added with a smile.
He was right. According to a report by the Turkish Journalists Association, 500 journalists were fired in Turkey in 2015; 70 others were subjected to physical violence. Thirty journalists remain in prison, mostly on charges of “terrorism.”
Needless to say, the unfortunate journalists are invariably known to be critical of Erdogan. There are also many journalists among the 1,845 Turks who have been investigated or prosecuted for insulting President Recep Tayyip Erdogan since he was elected in August 2014.
One of them is Sedat Ergin, editor-in-chief of Turkey’s most influential newspaper, Hurriyet. On March 25 Ergin had to appear before a penal court on charges of insulting Erdogan, with the prosecution demanding up to four years in jail for him. The veteran journalist says he is devastated to have been taken to court for the first time in his 41 years as a journalist on such an accusation. After his trial Ergin told reporters: “… in the year 2016 courthouse corridors and the hearing rooms have become the habitats of journalists in Turkey. Freedom of the press in Turkey in 2016 is now confined to court corridors.”
On that same day, two more journalists were in a courtroom, but they are not as lucky as Ergin in terms of the prison sentences demanded by the prosecution.
In May 2015, the secular daily newspaper Cumhuriyet published on its front page video and photographic evidence of arms deliveries by the Turkish intelligence services to Islamist groups in Syria. A month later, President Erdogan himself filed a criminal complaint against Cumhuriyet’s editor-in-chief, the prominent journalist, Can Dundar, and the newspaper’s Ankara bureau chief, Erdem Gul. In a public speech, Erdogan said: “He who ran this story will pay heavily for it.”
Dundar and Gul were arrested and remained behind bars for over 90 days, until Turkey’s Constitutional Court ruled that their detention violated their rights. They were released, but must now stand trial on charges of espionage, as well as aiding a terrorist organization that aims to topple Erdogan’s government. The case is a serious threat to the two journalists’ liberty, especially when Erdogan’s “weight” in the courtroom remains easily felt, if not seen.

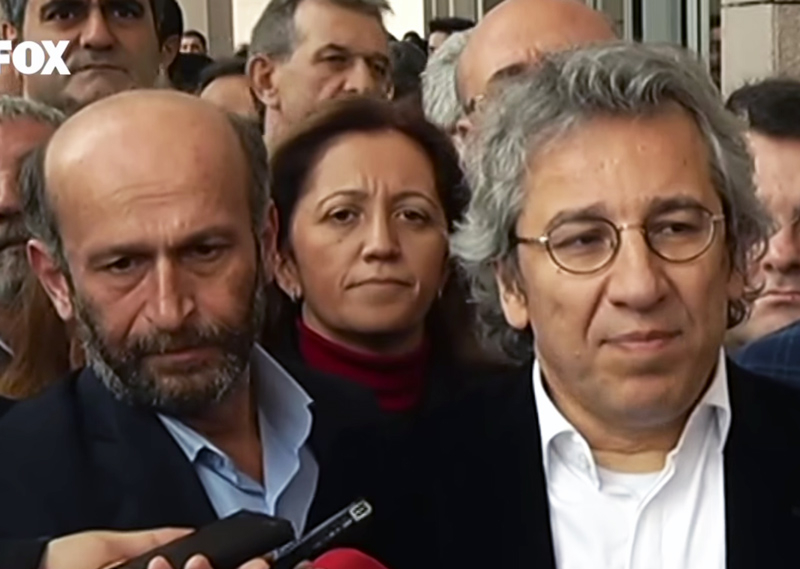
Can Dundar (right), editor-in-chief of Turkey’s Cumhuriyet newspaper, and Erdem Gul (left), Cumhuriyet‘s Ankara bureau chief, were arrested after the paper published evidence of arms deliveries by the Turkish intelligence services to Islamist groups in Syria. They remained behind bars for over 90 days, until Turkey’s Constitutional Court ruled that their detention violated their rights. |
At the March 25 hearing, the Istanbul court ruled for the whole trial to be held in secret. A group of opposition MPs protested the decision and refused to leave the courtroom. The court decided to file a criminal complaint against them for “obstructing justice.”
“We came here today to defend journalism. We gathered here before and said the same thing. We said we would defend the people’s right to access information. We defended that and we were arrested,” Dundar said.
It seems that Erdogan has no intention of leaving the journalists alone. The trial also clearly exhibits how his authoritarian rule diverges from Western democratic culture. On March 25, a group of Western consuls-general in Istanbul attended the journalists’ trial in a show of solidarity. The diplomats included Leigh Turner, the British Consul-General, who shared images from outside the court and messages of support for the journalists on Twitter. Now Erdogan thinks he has new enemies.
The day after the court hearing, Erdogan spoke:
“The situation of those who attended this hearing is very important. The consuls-general in Istanbul come to the courthouse. Who are you, what are you doing there? This is not your country, this is Turkey … Diplomats can operate within the boundaries of missions. Elsewhere is subject to permission.”
Now is that a new jurisprudence in diplomacy — that foreign diplomats in Turkey should be confined to their mission buildings and not observe most important political trials without permission from the Turkish government? In addition to the court’s blackout on the Dundar-Gul case, Erdogan now wants political confinement for the journalists.
By pursuing life sentences so aggressively for the journalists, Erdogan is in fact trying to achieve another political goal: He is giving messages at many wavelengths to any other investigative journalist who may in the future publish another embarrassing report on his administration.
Not really peaceful and free times for Turkish journalism.