Emmanuel Macron — whose victory in the French presidential election on May 7, 2017 was declared decisive — was presented as a centrist, a newcomer in politics with strong ties to the business world, and a man who could bring a new impetus to a stagnant country.
The reality, however, is quite different.
His victory was actually not “decisive”. Although he received a high percentage of the votes cast (66%), the number of voters who cast a blank ballot or decided to abstain was the highest ever in a French presidential election.
Although his opponent, Marine Le Pen, tried to dissociate herself from the anti-Semitism of her father, Jean-Marie Le Pen, she was treated as a walking horror by almost all politicians and journalists during the entire campaign. That she nevertheless drew 34% of the votes was a sign of the depth of the anger and frustration that has been engulfing the French people. More than half of those who chose Macron were apparently voting against Marine Le Pen, rather than for Macron.
Macron, who won by default, suffers from a deep lack of legitimacy. He was elected because he was the last man standing, and because the moderate right’s candidate, François Fillon, was sabotaged by a demolition operation carried out by the media and by a political use of justice. Significantly, the legal prosecution of Fillon stopped immediately after he was defeated.
Macron is not a centrist: he was discreetly supported throughout the campaign by most of the Socialist Party’s leaders and by the outgoing Socialist President, François Hollande. The day after the election, during a V-E Day ceremony, Hollande could not hide his joy. A few days later, on May 14, when he handed the office of the president over to Macron, Hollande said that what was happening was not an “alternative” but a “continuity”. All Macron’s team-members were socialists or leftists. Macron’s leading political strategist, Ismael Emelien, had worked for the campaign that led to the election of Nicolas Maduro in Venezuela.
Macron’s entire program is socialist. Proposals for additional public expenditures abound. “Climate change” is defined as “the key issue for the future of the world”. The proposed changes to the Labor Code and the tax system are largely cosmetic and seem intended more to give an illusion of change than to bring about real change. While Macron does not reject a market economy, he thinks that it must be placed at the service of “social justice”, and that the government’s role is to “guide”, to “protect”, “to help” — not to guarantee freedom to choose. Significantly, the economists who participated in the elaboration of Macron’s program are those who had drawn up Hollande’s economic program in 2012.
Even if he is young, Macron is not a newcomer to politics and does not embody renewal. He not only worked with Hollande for five years, but those who shaped his political ascent have long careers behind them: Jacques Attali was President François Mitterand’s adviser in the 1980s ; Alain Minc worked with all French Presidents since Valery Giscard d’Estaing was elected in 1974, and Jean-Pierre Jouyet was the cabinet director for Socialist Prime Minister Lionel Jospin in the late 1990s. Just after the election, three documentaries were broadcast on French television explaining in detail how Macron’s campaign was organized. Macron is the pure product of what analysts described as the “French nomenklatura” — an arrogant élite, composed of senior officials, political power-holders and the businessmen working in close collaboration with them.
Macron can only be described as close to the business world if one understands how things work in France. The French economy is a mixed system where it is almost impossible to succeed financially without having close relations with political leaders who can grant favors and subsidies, and either authorize, prohibit or facilitate contracts or hinder them.
During the years he spent at Hollande’s side, Macron helped various French businessmen. They thanked him by massively contributing to his campaign. It would be surprising if they do not expect a “return on investment”. The operation that allowed Macron’s election could be described in business language as a takeover. Almost all French private media outlets belong to those who supported Macron and were part of the takeover.
Macron is not supposed to bring any new impetus to business, but to ensure and consolidate the power of those who placed him where he is. Their goal is to create a large, single, center-left, technocratic political party that will crush the old political parties and that will be installed in a position of hegemony. The party’s slogan, “En Marche!” (“On the Move!”), was established to go forward in that direction; the old political parties have been almost destroyed. The official Socialist Party is dying. The main center-right party, The Republicans, is in disarray. One of its leaders, Edouard Philippe, was appointed Macron’s Prime Minister. Another, Bruno Le Maire, is now Finance and Economy minister: he will have to apply quite a different policy from those defined by his original party. The rightist National Front and the radical left will be treated as receptacles of anger: everything will be done so that they stay marginalized.
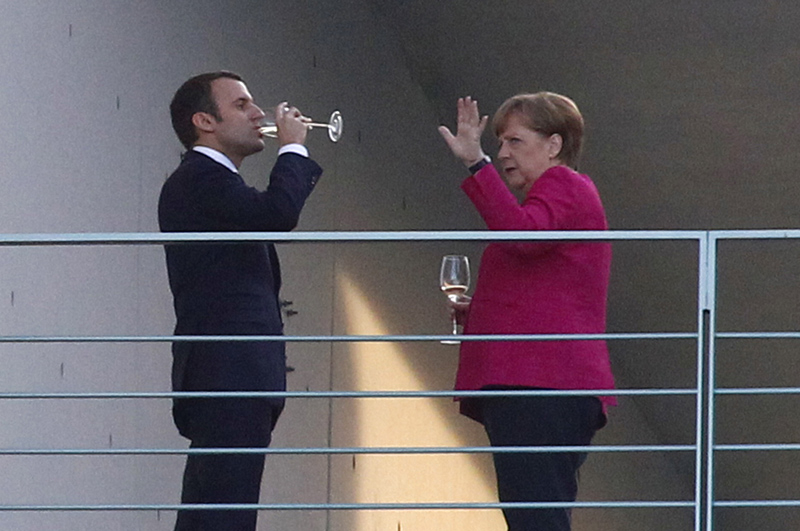
Another goal is to entrust ever more power to the technocratic unaccountable, untransparent and undemocratic institutions of the European Union: it is a goal Emmanuel Macron never stopped emphasizing. On May 7, as soon as the election result was known, the leaders of the European Union showed their enthusiasm. The president of the European Commission, Jean-Claude Juncker, spoke of “a signal of hope for Europe”. On May 15, immediately after the inauguration, Macron went to Berlin, met German Chancellor Angela Merkel and said that he hoped for a rapid “strengthening of the Union”. Macron says he wants the creation of an EU Ministry of Finance, whose decisions would have binding force for all member states.
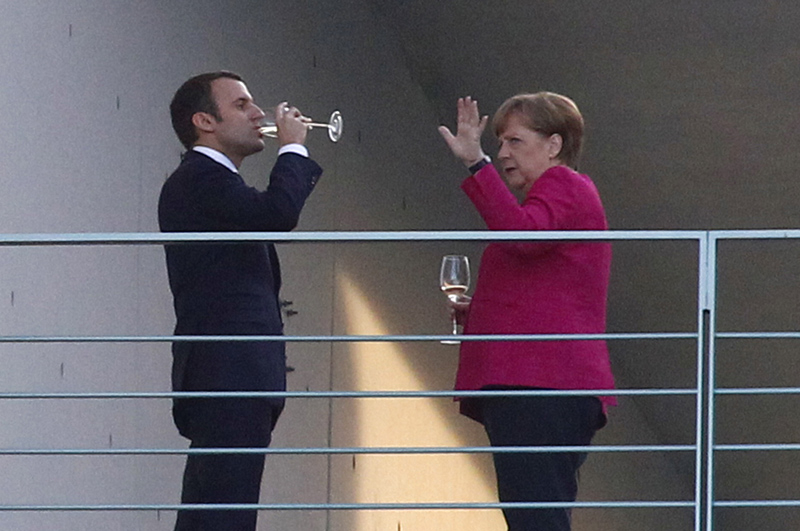

French President Emmanuel Macron and German Chancellor Angela Merkel chat in Berlin on May 15, 2017. (Photo by Michele Tantussi/Getty Images) |
A deliberate side-effect of Macron’s policies will be population change. Like many European leaders, Emmanuel Macron seems convinced that the remedy for the demographic deficit and the aging of ethnic European populations is more immigration. On September 6, 2015, he stated that “immigration is an opportunity for all of us”. On February 12, 2017, he said, “I will propose to the Algerian government the creation of a Franco-Algerian Bureau of Youth, to encourage mobility between the two shores of the Mediterranean”. A few weeks later, he declared that “the duty of Europe is to offer asylum to all those who seek its protection” and that “France must take its fair share of refugees”.
Almost all refugees arriving in France are Muslims. France already has the greatest percentage of Muslims in Europe. Macron wants Islam to have more room in France. His position concerning other religions is not known. His position on Islam is clear:
“Today, Muslims of France are poorly treated … Tomorrow, a new structure will make it possible to relaunch the work sites of the Muslim religion in France: the construction and the improvement of worthy places of worship will take place where their presence is necessary, and the training of imams of France will be organized.”
The French branch of the Muslim Brotherhood congratulated Macron on on his victory. It published an official communiqué saying: “Muslims think that the new President of the Republic will allow the reconciliation of France with itself and will allow us to go farther, together.”
Macron’s prime minister, Edouard Philippe, has close ties with the Muslim Brotherhood and favored their installation in the city of which he is the mayor, Le Havre. Richard Ferrand — a Socialist MP, the secretary-general of En Marche! since its inception, and now Minister for the Cohesion of Territories — has been financially contributing to the anti-Israel BDS movement and to “pro-Palestinian” organizations for years. Gerard Collomb, the Socialist Mayor of Lyon, and now Interior Minister, financed the French Institute of Muslim Civilization that will open its doors in December 2017.
In a recent article, Yves Mamou noted that Macron is not “an open promoter of Islamism in France” and could be defined as a “useful idiot.”
In another recent article, Bruce Bawer wondered how the French could have chosen Emmanuel Macron. His answer was that “the mainstream media have played a role”. Evidently, also, “some people do not want to know the truth,” even when the truth is in front of their eyes.
“Some people are accustomed to the idea that there are people above them in the hierarchy whose job is to think about, and take care of the big things while they, the citizens, the mice, take care of their own little lives”.
A majority of the French did not choose Macron but apparently accept that there are people above them. Those who do not accept this fact so easily are many, but in minority, and they are likely to become a smaller minority. Macron is counting on their resignation. It is not certain, however, that the millions of people who voted for Marine Le Pen, despite her extremely problematic closeness to Russia and the harsh campaign against her, or those who voted for the leftist candidates, will so easily give up. It is also not certain — thanks to willful blindness and appeasement — that Islamists will mellow, or that jihadist attacks will stop.
Macron said he was “dismayed” over Manchester Arena terror attack. He added that he was “filled with dread”. He did not express the necessity of confronting the danger. The French have every reason to be nervous.
Dr. Guy Millière, a professor at the University of Paris, is the author of 27 books on France and Europe.